No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
Home » Neurological Recovery Blog » Traumatic Brain Injury » Types of TBI » Hypothalamus Damage: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Last updated on September 8, 2022
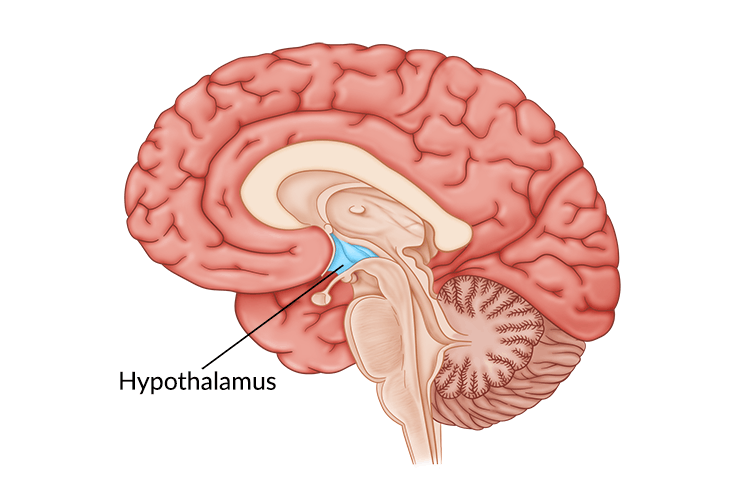
Hypothalamus damage can lead to a variety of endocrine disorders, such as diabetes insipidus and hypothyroidism. While treatment for a brain injury often involves rehabilitative therapy, treatment for a hypothalamus brain injury requires a different approach due to its role in hormone regulation.
This article will discuss the causes and symptoms of hypothalamus damage and some of the most effective management techniques. Use the links below to jump straight to any section.
The hypothalamus is a structure located in the center of the brain that serves as the primary link between the central nervous system and the endocrine system. The endocrine system is responsible for releasing different hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to help the body function properly. It is involved with different processes of the body including communicating with the autonomic nervous system (which controls automatic life-sustaining functions), developing the reproductive system, and regulating metabolism.
Additionally, the hypothalamus is responsible for maintaining homeostasis, or a balanced state of physiological processes. The body must maintain steady levels of certain vital functions in order to achieve homeostasis.
Functions controlled and regulated by the hypothalamus include:
The body sends signals to the hypothalamus alerting it when there is an imbalance in any one of these functions. The hypothalamus responds by releasing hormones to balance the body. Each hormone has a specific role but they all work together to achieve homeostasis.
While the hypothalamus drives the production and release of hormones, it most often does so by secreting “releasing hormones”. These travel directly below the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland, which then releases the hormones that travel throughout the body.
While there are many important hormones released by the hypothalamus, three examples include:
Damage to the hypothalamus can interfere with many biological processes, including homeostasis. Without the proper exchange of hormones, many organs cannot function properly. Therefore, it’s important to identify the cause of hypothalamus damage to receive the appropriate treatment.
The hypothalamus, particularly the anterior (front) side, is vulnerable to injury. Damage often occurs when the brain sustains a traumatic event including a head injury. Studies have shown that about 60% of traumatic brain injuries result in pituitary gland and/or hypothalamus damage. However, there are other medical conditions that can also cause hypothalamus damage.
Some of the most common causes of hypothalamus damage include:
Hypothalamus damage may also occur due to genetic disorders such as the Prader-Willi syndrome, the Kallmann syndrome, or birth defects. Although the causes of hypothalamus damage may vary, the symptoms are usually the same.
When hypothalamus damage is caused by a traumatic event, it can often be overlooked during brain injury treatment because the symptoms are similar to other types of brain injuries or medical conditions. Therefore, it’s important to understand the signs of a hypothalamus injury to help you differentiate between the symptoms and seek the proper medical care.
Common symptoms of hypothalamus damage include:
Symptoms of hypothalamus damage may evolve over time. Be sure to follow-up with your doctor if you notice any new or recurring symptoms after a brain injury to obtain a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
The hypothalamus is versatile meaning it plays a role in many different functions of the body. For this reason, when the hypothalamus sustains damage, it can result in various health conditions or complications.
Some of the most common health conditions caused by hypothalamus damage include:
Hypothalamus damage can also lead to extreme fluctuations in body temperature. The hypothalamus plays a critical role in stabilizing the body’s core temperature. For example, when the body’s temperature is above 98.6° F, the hypothalamus signals the sweat glands to help the body cool down. Other cooling responses by the hypothalamus include increasing water retention and dilating blood vessels.
However, when the hypothalamus becomes injured, it can no longer accurately control your temperature. Therefore, you may experience frequent hot or cold flashes. A prolonged increase in core body temperature can lead to further brain damage. That’s why it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible.
Treatment for hypothalamus damage may vary depending on the diagnosis. To obtain a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, your medical team will perform a combination of different lab tests.
Hypothalamic dysfunction after brain injury may be measured by heart rate variability (HRV). To perform this exam, your doctor will give you a Holter monitor that records heart function over the course of 24 hours. Electrodes are placed on your chest to allow you to continue with your daily activities during this period.
The HRV measures how much your heart rate fluctuates. Changes indicate that the endocrine system is functioning well and keeping the body regulated. If there are very few or no changes it can indicate hypothalamus dysfunction. When the heart rate is either consistently high or low, it’s because there is limited communication between the body’s sympathetic and parasympathetic responses, which are controlled by the hypothalamus.
Other exams used to diagnose hypothalamus damage may include:
With a proper diagnosis of hypothalamus damage your doctor can start you on hormone therapy to replace any deficiencies, or provide different forms of treatment.
Treatment for hypothalamus damage involves replacing lost hormones. Therefore, it’s important for all individuals to check their hormonal levels with their doctor as soon as possible after sustaining hypothalamus damage.
Some of the most common hormones your doctor may suggest to increase include:
Many of these hormones may need to be taken daily to help regulate the body and compensate for hypothalamus damage. Along with hormonal therapy, there are other management techniques that can help with a hypothalamus brain injury.
Management for hypothalamus damage may also include:
Every brain injury is different, and while many survivors may experience similar symptoms, treatment will vary for everyone. Speak with your doctor to ensure which course of treatment is safe and suitable for your condition.
Hypothalamus damage can occur due to various conditions such as a head injury, tumor, and immune diseases. The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in many of our bodily functions which can be lost after a traumatic event such as a head injury or tumor.
Fortunately, many of these functions can be improved and restored with hormonal therapy. The sooner you seek treatment, the higher the chances of improving hypothalamus damage.
We hope this article helped you understand how hypothalamus damage can occur, and encouraged you to seek the proper medical care.

If you like our content, you’ll love our ebook and newsletters! Get instant access to our TBI recovery tips ebook with 20 pages of helpful advice by signing up below.
You’ll also receive our emails that share survivor stories and more useful TBI recovery tips, which you can opt out of at any time. (We know you’ll love them, too.)
We will never sell your email address, and we never spam. That we promise.


Time with a speech therapist is extremely valuable during recovery, especially if you struggle with communication, critical thinking, or memory after brain injury. Insurance typically covers speech therapy for a fixed amount of time. But once it’s over, recovery is in your hands.
That’s why a team of neuroscientists and clinicians from Boston University created the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy app. Designed for those recovering from stroke, TBI, or living with neurological conditions, the app contains over 100,000 cognitive exercises that are all available right from your phone or tablet. That’s like having a speech therapist by your side whenever you want!
This app is the perfect fit if you want to improve your speaking, memory, or general mental sharpness. And, it’s affordable at just $29.99/month!
“For the past 6 months, my son has used the app about three times a week. The app is like a virtual therapist, it’s very easy to use, and it gives him immediate feedback.
He now understands things faster, can make decisions with less hesitation, has improved recognition of words, and his confidence is higher. I also find it easy to get in touch with customer service; they pleasantly help out. The whole experience has been great.”
— Miriam
With the CT App, you can get the guidance you need right from your phone or tablet. You can use it on your own or in between sessions with your speech therapist.
Whether you struggle with aphasia, memory loss, or critical thinking, the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy App can help.
“The CT app has helped me gather my confidence by building on and reinforcing old forgotten skills. It helps to see my percentages increase, and work harder when they decrease. It’s very self-motivating.” -Kathryn
We are confident that this app will help improve your speech and cognitive function after brain injury. Like our recovery tools, the CT App is also covered by our 30-day money-back guarantee.

Do you know these 15 TBI recovery tips?
Get a free copy of our ebook 15 Things Every TBI Survivor Must Know. Click here to get instant access.
Grab a free rehab exercise ebook!
Sign up to receive a free PDF ebook with recovery exercises for stroke, traumatic brain injury, or spinal cord injury below: