No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
Home » Neurological Recovery Blog » Traumatic Brain Injury » Coup-Contrecoup Injury: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Last updated on August 12, 2021
Coup-contrecoup brain injuries occur when a head injury results in damage to 2 sides of the brain (the side of the trauma and the opposite side of the brain). Because they affect multiple areas of the brain, coup-contrecoup injuries can result in various secondary complications and are one of the most serious types of traumatic brain injury.
To help you understand what recovery from a coup-contrecoup brain injury entails, this article will discuss:
The terms coup and contrecoup are French for “blow” and “counterblow.” Therefore, a coup-contrecoup injury actually refers to two separate brain injuries sustained during the same incident.
A coup injury refers to the brain damage that occurs directly under the point of impact. In contrast, a contrecoup injury occurs on the opposite side of the brain from where the head is struck. These injuries can occur separately (as only a coup injury or only a contrecoup injury), but if the blow is strong enough, they usually appear together (as a coup-contrecoup injury).
The brain is encased within the skull and floats in cerebrospinal fluid. Generally, this provides enough protection from the bumps and jolts we experience throughout the day. However, when the force of a blow to the head is severe enough, the brain can slam against the skull, causing serious damage.
Most coup-contrecoup injuries occur when the person’s head slams against a stationary object. For example, if a car hits you from behind, you may experience whiplash and hit your head against the steering wheel.
When the skull hits the object, the brain moves toward the object until it collides with the skull. Then, due to the impact of the initial trauma, it rebounds, causing the second impact to the brain due to hitting the opposite side of the skull. This is demonstrated in the video below.
Coup-contrecoup injuries are considered focal brain injuries, meaning that they are confined to specific areas of the brain. In the following section, we’ll discuss the various signs and symptoms an individual may experience after coup-contrecoup brain injury.
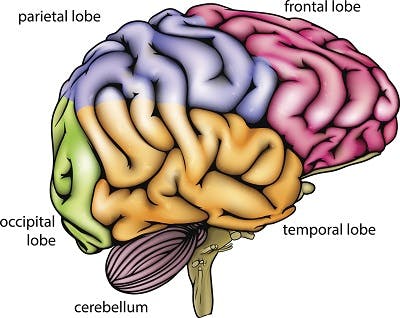
Coup-contrecoup brain injuries may affect any 2 regions of the brain. In fact, many coup-contrecoup lesions are not exactly opposite to one another. As a result, individuals may experience a wide range of secondary effects depending on which regions of the brain are affected.
Each hemisphere of the brain is divided into 4 lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. Most brain functions involve the collaboration of various regions of the brain. However, generally there is a specific region that each function can be primarily attributed to (the region that plays the greatest role in regulating that function).
Below, we’ll discuss common signs and symptoms of damage to each of these regions of the brain.
Want 20 pages of brain injury recovery tips in PDF form? Click here to download our free ebook “15 Things Every TBI Survivor Must Know” (link opens a pop up for uninterrupted reading)
The frontal lobe takes up the largest area of the cerebral cortex. It is primarily responsible for higher cognitive skills, such as attention, planning, memory, and behavior.
A coup-contrecoup injury that damages the frontal lobe may result in the following functional challenges:
Additionally, damage to the frontal lobe may impair motor control. As a result, individuals may experience weakness or paralysis of voluntary muscle movements.
The parietal lobe is located behind the frontal lobe. This region of the brain is responsible for processing sensory information such as touch and proprioception (your sense of where your body is in space). If a coup-contrecoup injury affects the parietal lobe, it may cause problems with sensation and perception. As a result, individuals may struggle to interact with their surroundings.
Common symptoms of parietal lobe damage include:
Behind the parietal lobe and towards the back of the brain resides the occipital lobe. This region of the brain is primarily responsible for processing visual stimuli.
A coup-contrecoup injury that affects the occipital lobe may involve different types of blindness and visual distortions, such as:
The temporal lobe is located in the lower middle part of the brain, next to your temples and above the ears. Its main responsibility is processing auditory information, but it also plays a role in interpreting smell and sight.
A coup-contrecoup injury that affects the temporal lobe may result in:
Because coup-contrecoup brain injuries may affect any region of the brain, individuals may also experience other common secondary effects of brain injury, including:
Now that you understand the potential outcomes of a coup-contrecoup brain injury, the following section will discuss how to treat one.
Treatment of coup-contrecoup injuries primarily depends on the severity of the injuries and which regions of the brain are affected. Every coup-contrecoup brain injury is unique, so a personalized approach to treatment that targets each individual’s specific secondary effects is ideal.
Frequently recommended rehabilitative interventions include:
To improve outcomes after a coup-contrecoup injury, it is essential to practice rehabilitative exercises and activities as much as possible. This will stimulate the brain, reinforce demand for those functions, and promote neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to rewire itself).
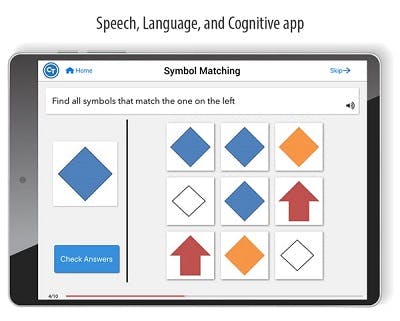
One way to perform as many repetitions as possible is to download an app on your phone or tablet, such as the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy App. It provides access to over 100,000 speech and cognitive therapy exercises designed by speech therapists so you can practice whenever you want.
Additionally, the CT App targets a variety of functions including listening, speaking, attention, memory, and visual processing. This makes it ideal for all coup-contrecoup injury survivors, regardless of which regions of the brain are affected.

Likewise, if a coup-contrecoup injury has affected your movements, it may be worth investing in home rehab devices like the FitMi to retrain the brain to move again. FitMi includes 40 exercises for the leg, core, arm, and hand. They’re all designed by physical and occupational therapists to strengthen and improve motor control over muscles affected by brain injury.
Here’s what a caregiver said about FitMi during her son’s brain injury recovery:
“My son Sam has a TBI as a result of being hit by a car 5 years ago. We were looking for some way to get him to move since he would prefer to sit on the couch all day. He works with the FitMi on his own without anyone telling him to, and that is saying a lot. Any moving he does is good for him, and the FitMi is geared for reps of movements to help him continue to regain mobility. Best investment we have made since he left rehab!” — Ann L.
FitMi works best when used daily at home between outpatient therapy sessions. It helps fill in the gap when you can’t see your therapist daily or when insurance stops covering the sessions you need to continue improving.
Coup-contrecoup brain injuries affect both the site of impact and the opposite side of the brain. Because two regions of the brain are affected, individuals with coup-contrecoup injuries may experience a wide range of secondary effects. Treatment will vary depending on which regions of the brain are affected and their subsequent effects.
We hope this article helped you understand the implications of a coup-contrecoup brain injury as well as the best practices for recovering from one.

If you like our content, you’ll love our ebook and newsletters! Get instant access to our TBI recovery tips ebook with 20 pages of helpful advice by signing up below.
You’ll also receive our emails that share survivor stories and more useful TBI recovery tips, which you can opt out of at any time. (We know you’ll love them, too.)
We will never sell your email address, and we never spam. That we promise.


Time with a speech therapist is extremely valuable during recovery, especially if you struggle with communication, critical thinking, or memory after brain injury. Insurance typically covers speech therapy for a fixed amount of time. But once it’s over, recovery is in your hands.
That’s why a team of neuroscientists and clinicians from Boston University created the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy app. Designed for those recovering from stroke, TBI, or living with neurological conditions, the app contains over 100,000 cognitive exercises that are all available right from your phone or tablet. That’s like having a speech therapist by your side whenever you want!
This app is the perfect fit if you want to improve your speaking, memory, or general mental sharpness. And, it’s affordable at just $29.99/month!
“For the past 6 months, my son has used the app about three times a week. The app is like a virtual therapist, it’s very easy to use, and it gives him immediate feedback.
He now understands things faster, can make decisions with less hesitation, has improved recognition of words, and his confidence is higher. I also find it easy to get in touch with customer service; they pleasantly help out. The whole experience has been great.”
— Miriam
With the CT App, you can get the guidance you need right from your phone or tablet. You can use it on your own or in between sessions with your speech therapist.
Whether you struggle with aphasia, memory loss, or critical thinking, the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy App can help.
“The CT app has helped me gather my confidence by building on and reinforcing old forgotten skills. It helps to see my percentages increase, and work harder when they decrease. It’s very self-motivating.” -Kathryn
We are confident that this app will help improve your speech and cognitive function after brain injury. Like our recovery tools, the CT App is also covered by our 30-day money-back guarantee.

Do you know these 15 TBI recovery tips?
Get a free copy of our ebook 15 Things Every TBI Survivor Must Know. Click here to get instant access.
Grab a free rehab exercise ebook!
Sign up to receive a free PDF ebook with recovery exercises for stroke, traumatic brain injury, or spinal cord injury below: