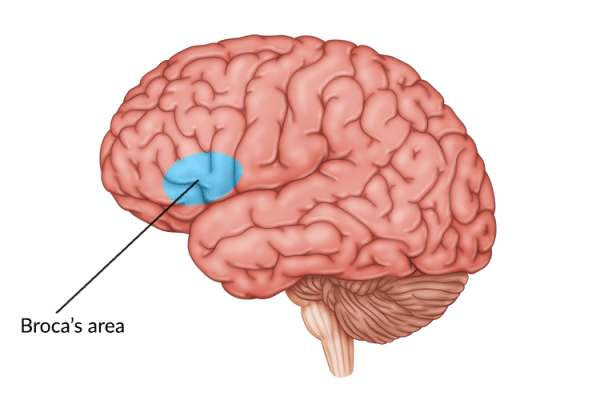
TBI and Depression: Causes, Signs, & Recovery Methods for Depression After Brain Injury
After sustaining a traumatic brain injury (TBI), survivors may experience feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or prolonged fatigue, which are all common symptoms of depression. It