No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.
Home » Neurological Recovery Blog » Traumatic Brain Injury » Cerebellum Brain Damage: What Causes It & How Rehabilitation Works
Last updated on March 21, 2022
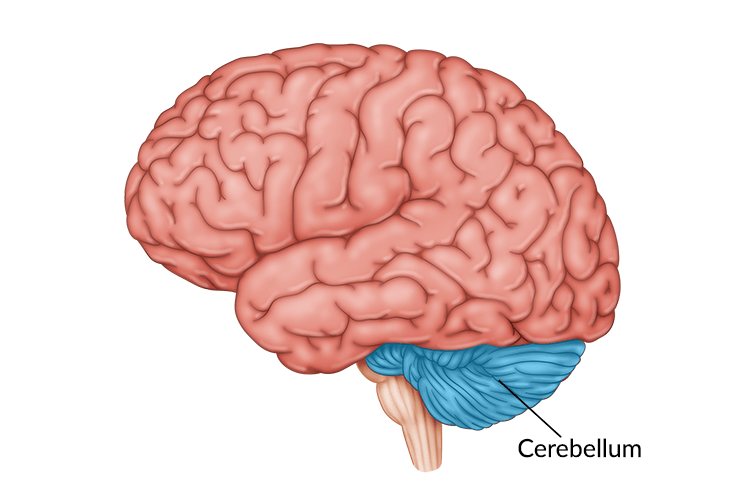
Although cerebellum brain damage is relatively rare, its effects can be quite serious. Damage to the cerebellum can result in significant motor, visual, and cognitive changes. However, with the appropriate treatment, individuals may be able to recover affected functions.
In this article, we’ll discuss the effects of cerebellum brain damage and treatment techniques to promote recovery. Use the links below to jump straight to any section:
The cerebellum (Latin for “little brain”) is located on the base of the brain, directly behind the brain stem. While the cerebellum makes up only about 10% of the brain’s mass, it contains anywhere from 50% to 80% of the total number of neurons (brain cells) in the brain.
One of the major responsibilities of the cerebellum is to fine-tune and coordinate voluntary movements. This is essential for maintaining balance, muscle tone, and posture. The cerebellum is also vital in coordinating the movements necessary for walking and other daily activities.
The cerebellum is crucial to several other functions, including cognition, language learning, eye movement, and reflexes. This means that cerebellum brain damage can affect all these functions and many others.
Because of the cerebellum’s location, it is fairly protected from external forces. Cerebellum brain damage often occurs due to anoxic brain injury, neurodegenerative disorders, or infection. Alcohol abuse can also cause the cerebellum to deteriorate.
When the cerebellum sustains damage, the signals it sends throughout the body become weaker or can cease entirely. This disruption is what leads to the various secondary effects associated with cerebellar damage.
An injury to the cerebellum can lead to a wide range of symptoms. The following are some of the most common cerebellum brain damage secondary effects:

In order to fine-tune movements, the cerebellum sends inhibitory or excitatory signals to various muscle groups. However, when the cerebellum is damaged, the timing of the messages sent from the cerebellum to the muscles is affected. This results in a lack of coordination known as apraxia.
For example, to pick up a fork, the brain must tell the triceps to activate in order to extend your arm. Your bicep muscle cannot fire while this is happening. Otherwise, your elbow would bend at the wrong time and you’d potentially miss the fork. Therefore, the cerebellum sends inhibitory signals to your bicep while allowing your triceps to easily extend your arm.
Apraxia can affect any movement that requires coordination, making many daily activities much more difficult. Many individuals with apraxia walk with a wide, staggering gait and require extra time to complete simple movements.
Apraxia can also affect your facial muscles and even your tongue, which can cause problems with slurred speech and swallowing.
Other motor effects that may result from cerebellum brain damage include:
The wide variety of motor challenges that can occur after cerebellum brain damage illustrates the depth of the cerebellum’s involvement in many complex motor functions.

Since balance depends on the continuous coordination of several muscle groups, cerebellar damage can lead to severe balance issues. This can affect your ability to walk, climb stairs, or change positions.
You might have trouble holding yourself upright when sitting or standing or feel a strong sense of dizziness. Balance exercises for brain injury and vestibular therapy are excellent ways to address balance problems.
Not only does the cerebellum plays a role in coordinating and perfecting muscle movements of the body, but it’s also responsible for controlling eye movements. Following cerebellum brain damage, the eye may make rapid, uncontrolled movements, a condition known as nystagmus.
There are three main types of eye movement a person with nystagmus can experience after cerebellum injury:
These movements can occur in one or both eyes and may cause your field of vision to appear scattered. Nystagmus can also cause severe dizziness after head injury.
Of note, the cerebellum also helps to regulate other visual functions, such as the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). The VOR is what allows you to continue seeing a stable picture even when while you are moving around. These visual functions may also be affected by cerebellum brain damage.
The cerebellum is involved with the coordination of the muscles involved in speech articulation as well as some the cognitive components of language.
One common speech disorder associated with cerebellum brain damage is ataxic dysarthria. Ataxic refers to a lack of motor control, while dysarthria refers to difficulties coordinating the muscles involved in speaking. This may result in scanning speech, which may be slow, slurred, and/or disjointed.
Although traditionally cerebellum brain damage was thought to only affect motor functions, research has shown that it can also impact a person’s cognitive functions.
Some of the areas that cerebellum brain damage affects include:
Using a combination of speech therapy activities and cognitive rehab exercises can improve your cognitive functions.

When cerebellum brain damage occurs, the signals that the cerebellum is responsible for transmitting are disrupted. Since the cerebellum plays such as large role in motor coordination, this most often means that muscles are not receiving the signals needed to coordinate movements.
Therefore, individuals must improve the communication between their brain and the rest of the body to recover affected functions. This is possible by completing repetitious exercises to activate the brain’s natural repair mechanism, neuroplasticity.
When you practice a task, even if it is not performed perfectly, your brain forms neural pathways associated with that task. As you continue practicing, these pathways become stronger. Over time, the brain may regain its ability to easily use these new neural pathways to communicate with the muscles, allowing you to coordinate movement again.
Since cerebellum brain damage can affects each person differently, the treatment required for recovery may vary. However, most individuals following cerebellum brain damage benefit from physical, occupational, and/or speech therapy. The focus of each of these therapies is to activate neuroplasticity to promote recovery.
Physical therapists may focus on improving balance and coordination through retraining the brain. They may use strengthening exercises and progressively more challenging activities (such as static standing, standing on uneven surfaces, then walking on uneven ground) to promote functional recovery. Some physical therapists specialize in vestibular therapy, which can help individuals who struggle with dizziness and balance.

Occupational therapists focus on helping individuals complete their daily activities. They may encourage individuals who have apraxia to practice each step of an activity separately before putting them all together. They may also recommend using compensatory strategies and adaptive equipment. Vision therapy is a specialty area of some occupational therapists that may help with nystagmus and other visual concerns.
Speech therapists can provide exercises to improve coordination of oral musculature affected by ataxic dysarthria. They can also help with recovering or compensating for lost cognitive functions.
The more you practice affected functions, the more your brain will create new neural pathways to promote improvements.
Cerebellar brain damage can cause significant problems with muscle coordination. Fortunately, recovery is possible.
The key to healing any brain injury, including cerebellar injuries, is to engage your brain’s neuroplasticity. Completing therapy exercises daily can promote improvements in your balance, coordination, and cognitive skills. You may even experience a full recovery, depending on how severe your injury was. We hope this guide to cerebellum brain damage gives you the tools you need to make a great recovery.

If you like our content, you’ll love our ebook and newsletters! Get instant access to our TBI recovery tips ebook with 20 pages of helpful advice by signing up below.
You’ll also receive our emails that share survivor stories and more useful TBI recovery tips, which you can opt out of at any time. (We know you’ll love them, too.)
We will never sell your email address, and we never spam. That we promise.


Time with a speech therapist is extremely valuable during recovery, especially if you struggle with communication, critical thinking, or memory after brain injury. Insurance typically covers speech therapy for a fixed amount of time. But once it’s over, recovery is in your hands.
That’s why a team of neuroscientists and clinicians from Boston University created the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy app. Designed for those recovering from stroke, TBI, or living with neurological conditions, the app contains over 100,000 cognitive exercises that are all available right from your phone or tablet. That’s like having a speech therapist by your side whenever you want!
This app is the perfect fit if you want to improve your speaking, memory, or general mental sharpness. And, it’s affordable at just $29.99/month!
“For the past 6 months, my son has used the app about three times a week. The app is like a virtual therapist, it’s very easy to use, and it gives him immediate feedback.
He now understands things faster, can make decisions with less hesitation, has improved recognition of words, and his confidence is higher. I also find it easy to get in touch with customer service; they pleasantly help out. The whole experience has been great.”
— Miriam
With the CT App, you can get the guidance you need right from your phone or tablet. You can use it on your own or in between sessions with your speech therapist.
Whether you struggle with aphasia, memory loss, or critical thinking, the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy App can help.
“The CT app has helped me gather my confidence by building on and reinforcing old forgotten skills. It helps to see my percentages increase, and work harder when they decrease. It’s very self-motivating.” -Kathryn
We are confident that this app will help improve your speech and cognitive function after brain injury. Like our recovery tools, the CT App is also covered by our 30-day money-back guarantee.

Do you know these 15 TBI recovery tips?
Get a free copy of our ebook 15 Things Every TBI Survivor Must Know. Click here to get instant access.
Grab a free rehab exercise ebook!
Sign up to receive a free PDF ebook with recovery exercises for stroke, traumatic brain injury, or spinal cord injury below: