Anterior cingulate cortex damage can result in different cognitive, emotional, and even physical effects. For example, someone with damage to the anterior cingulate cortex may sustain cognitive impairments such as poor decision-making skills or they may develop emotional effects such as a lack of empathy.
In this article, you will learn the basic functions of the anterior cingulate cortex, what happens when anterior cingulate cortex damage occurs, and how the recovery process works.
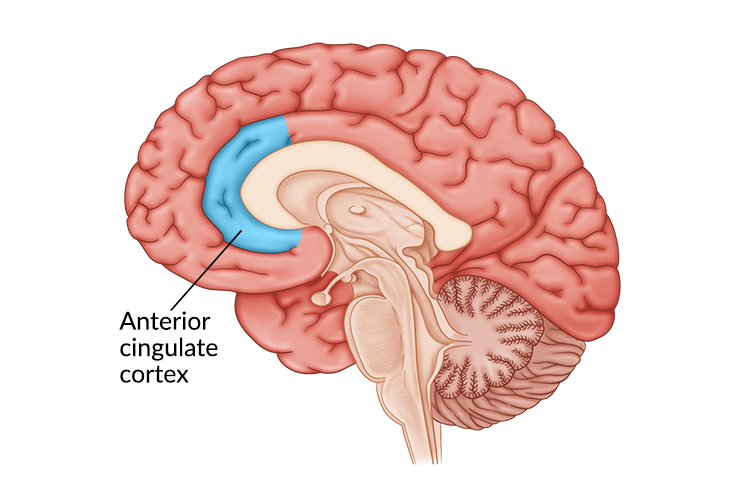
Anterior Cingulate Cortex Function
The anterior cingulate cortex is located near the front of the brain and wraps around the head of the corpus callosum. It connects to other brain regions and therefore participates in a wide variety of functions.
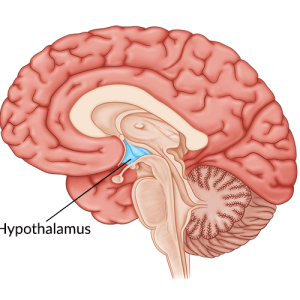
For example, the anterior cingulate cortex connects to limbic structures such as the amygdala and hypothalamus, which are responsible for processing emotions. Because of this, the cingulate cortex plays a valuable role in emotional functions such as:
- Assigning emotions to certain stimuli or events
- Connecting facial expressions to the correct emotion
- Making vocalizations to express certain emotions (e.g., laughing when you are happy)
The anterior cingulate cortex is also involved in pain perception and regulating endocrine responses such as stress and cortisol levels. Finally, there are parts of the anterior cingulate cortex that play a role in cognitive functions such as decision-making, attention, and memory.
Since the anterior cingulate cortex plays a role in such a wide range of functions, damage to this area of the brain can lead to a diverse array of secondary effects.
Secondary Effects of Anterior Cingulate Cortex Damage
The effects of anterior cingulate cortex damage can be divided into three groups: cognitive, emotional, and physical. Not all individuals will experience impairments in all three domains, however. Secondary effects depend on the severity and location of the damage.
Here are the most common effects that can occur after anterior cingulate cortex damage:
Autonomic Dysfunction
The anterior cingulate cortex collaborates with the hypothalamus to regulate hormone release. When we experience emotions such as fear or anger, the hypothalamus and anterior cingulate cortex work together to coordinate autonomic functions or involuntary (automatic) bodily processes.
When the anterior cingulate cortex becomes damaged, this may result in autonomic dysfunction, meaning that the autonomic nervous system cannot function properly. This can affect involuntary bodily processes such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion, among many others.
Flat Affect
The anterior cingulate cortex plays a strong role in overall affect, or emotional expressiveness. This area of the brain helps translate emotion into physical expression. It can do this because many of its neural connections are linked to the limbic system, the source of emotions.
Therefore, after anterior cingulate cortex damage, a person may have trouble expressing their feelings or responding emotionally to different situations. This can contribute to a lack of emotion, formally known as “flat affect.”
Lack of Empathy
Empathy is a skill regulated in part by both the anterior cingulate cortex and the amygdala, a part of the brain that contributes to emotional information processing. These two areas of the brain work together to pair emotions with memory and sensory information, which helps a person develop empathy. This process allows an individual to imagine what someone else is feeling or experiencing.
Anterior cingulate cortex damage can inhibit this process, leading to a lack of empathy as well as difficulty with social awareness or behavior. For example, the individual may struggle to associate certain actions with emotions such as fear or sadness. This can lead to socially inappropriate behavior because the person does not realize that their actions can be hurtful or distressing to others.
Panic Disorder
A person’s cognitive and emotional response to stimuli is also regulated in part by the anterior cingulate cortex. When this area of the brain becomes damaged, it can contribute to panic disorder. This is a type of anxiety disorder that involves sudden, intense attacks of panic or fear. This can affect an individual’s daily life and participation in social or community activities.
Poor Decision-Making
The decision-making process is assisted by the anterior cingulate cortex. It allows us to assess the risks and payoffs of our actions so that we can make informed, dynamic decisions. It also allows us to respond to potentially harmful stimuli to help keep us safe. Without this skill, a person’s judgment can be impaired and, in severe cases, the person may put themselves into dangerous situations.
A common misunderstanding of individuals with traumatic brain injury occurs when survivors with impaired decision-making skills are judged as being careless. However, poor decision-making or irrational decisions are often not the person’s fault. When a brain injury affects the areas of the brain responsible for decision-making, such as the anterior cingulate cortex, it can impair the brain’s ability to learn from mistakes.
Impaired Attention
In situations involving high conflict, distracting stimuli, and error processing, the anterior cingulate cortex plays an active role. It enables a person to shift their attention in order to respond to stimuli. When the anterior cingulate cortex sustains damage, survivors may develop attention deficits such as the inability to maintain attention when distractions are present.
Executive Dysfunction
Executive dysfunction is an umbrella term for a condition involving a wide array of cognitive, emotional, and behavioral changes. Executive dysfunction may include, but is not limited to:
- Impaired memory
- Lack of motivation
- Loss of cognitive flexibility
- Impulsivity
- Decreased attention
- Difficulty navigating conflict
Studies have shown that executive dysfunction may occur after damage to the anterior cingulate cortex. This further illustrates how the anterior cingulate cortex plays a strong role in emotion, behavior, and many different cognitive functions.
Treating Anterior Cingulate Cortex Damage
When damage to the anterior cingulate cortex causes physical effects such as autonomic dysfunction, the individual must work closely with their doctor and/or endocrinologist to monitor and manage symptoms. They may need to administer a variety of treatments depending on the symptoms, such as prescribing medication to stabilize blood pressure or heart rate.
Additionally, many of the effects of anterior cingulate cortex damage are cognitive and emotional. In this case, a psychotherapist, occupational therapist, and/or speech therapist are great resources for identifying the best treatment plan.
Some possible treatments that a therapist might recommend for survivors with anterior cingulate cortex damage include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy: This type of psychotherapy helps people better understand their behavior and develop positive strategies to avoid harmful actions. It can be especially helpful for patients who struggle with poor decision-making or lack of empathy.
- Speech therapy: A speech therapist can help individuals who struggle with flat affect relearn how to display appropriate emotions. For example, they can teach survivors how to control the pitch and tone of their voice again or practice facial expressions and movements.
- Medications: There are no drugs to treat anterior cingulate cortex damage specifically, but there are medications that can treat some symptoms. For example, some doctors may prescribe ADHD medications such as Adderall to help address executive dysfunction or impaired attention after brain injury.
Furthermore, therapists can often help individuals improve some of the cognitive effects of anterior cingulate cortex damage by providing cognitive rehab exercises. For example, if decision-making has become impaired, a therapist can prescribe exercises that require decision-making skills.
Practicing these exercises on a consistent basis helps stimulate adaptive changes in the brain through neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to build new connections and become more efficient. Therefore, by practicing the cognitive skills that are impaired, the survivor can maximize their chances of improving those skills and behaviors.
Understanding Anterior Cingulate Cortex Damage
The anterior cingulate cortex plays a crucial role in many cognitive, emotional, and physical functions. As a result, damage to this structure can cause a wide range of problems such as autonomic dysfunction, executive dysfunction, flat affect, and more. Fortunately, many of these impairments can be treated with the right rehab plan, such as cognitive rehabilitation with an occupational or speech therapist. We hope this article helps you better understand the effects of anterior cingulate cortex damage and how to overcome them.