Left hemiplegia describes paralysis of the left side of the body due to neurological injury. This secondary effect commonly occurs following a stroke or traumatic brain injury and can have a major impact on daily function. Luckily, many individuals with left hemiplegia have the potential to regain mobility on their affected side and improve their overall quality of life.
While hemiplegia can affect either side of the body, this article will specifically address hemiplegia on the left side. We will review the causes of left hemiplegia, common symptoms, recovery time, and treatment options. To help you navigate this article, feel free to use the jump links below:
What is Left Hemiplegia?
Left hemiplegia refers to paralysis or severe weakness on the left side of the body, often caused by damage to the right side of the brain It is the result of tissue damage to the nervous system. While it is most common following injury to the brain (such as a stroke or traumatic brain injury) left hemiplegia can also occur after injury to the spinal cord or peripheral nerves.
It is important to remember that left hemiplegia refers to paralysis of the left side. Another similar term, hemiparesis, refers to weakness of one side of the body and is less severe than hemiplegia. These terms are not interchangeable but are both common secondary effects after neurological injury.
Movement is the result of motor signals traveling between the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and muscles. These motor signals are responsible for controlling muscle activation and coordination, which produces intentional movement. When any of these pathways become damaged, individuals may experience resulting weakness or paralysis.
Causes of Left Hemiplegia
Some common causes of left hemiplegia include:
- Stroke
- Brain cancer
- Cerebral palsy
- Traumatic brain injury
- Spinal cord injury
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain infection
Each hemisphere of the brain controls movement on the opposite side of the body. For example, the brain’s right hemisphere controls movement on the left side of the body. This is why the two common causes of left hemiplegia are right hemisphere stroke and right hemisphere brain injury. So an injury to the right side of the brain, specifically the motor cortex, causes hemiplegia on the left side of the body.
However, unlike the brain, each side of the spinal cord controls movement on the same side of the body. Therefore, when a spinal cord injury causes left hemiplegia—a rare condition known as Brown-Séquard Syndrome—it results from damage to the left side of the spinal cord.
Paralysis on the left side of the body may place individuals at risk of experiencing additional complications. To help you understand what to expect, the following sections will discuss specific symptoms of left hemiplegia as well as potential effects that may occur alongside this condition.
Left-Sided Hemiplegia Symptoms
Generally, individuals with left hemiplegia experience difficulties associated with:
- Lack of active movement
- Abnormal muscle tone
- Impaired balance.
For example, everyday movements such as sitting upright, standing, walking, and weight transference may become more challenging.
This is because hemiplegia can affect the entire left side of the body, not just the limbs. That means left hemiplegia also affects the trunk and postural muscles, which has a negative impact on balance, proprioception, and overall stability. In addition, it commonly involves the muscles of the face as well, leading to difficulties with speech, facial expression, and eating.
When half of the body becomes paralyzed, it forces the unaffected regions of the body to work harder to perform everyday activities. Consequently, individuals may experience greater levels of fatigue due to the increased energy requirements necessary to perform once-simple tasks.
Some functions like writing or using eating utensils may not be affected by left hemiplegia for individuals that are right handed. As a result, for activities that are affected, survivors are often tempted to use only their unaffected side to improve efficiency and decrease frustration. However, it’s important for individuals to continue incorporating their left side during daily activities to avoid learned non-use.
Secondary Effects and Symptoms That May Accompany Left Hemiplegia
When left hemiplegia is caused by damage to the right side of the brain, individuals may experience additional secondary effects associated with right hemisphere brain injury or stroke. Let’s take a look at some of the additional symptoms of left hemiplegia following a right hemisphere stroke.
Left Neglect
Left neglect refers to a survivor’s lack of awareness of the left side of their environment, including the left side of their body. This spatial awareness deficit commonly accompanies left hemiplegia and can impact many functions of daily life. For example, survivors with left neglect may only eat from the right side of their plate, bump into objects on their left side, or seem to ignore conversations happening on the left side of their environment.
Attention Problems
The right hemisphere of the brain is responsible for attention and cognition. Following tissue damage, survivors may note that it is challenging to focus on a task, think through logical steps, or follow a conversation as these processes have been disrupted. This can be frustrating as individuals pursue recovery from left hemiplegia.
Memory Problems
Another secondary effect can include memory problems. Tissue damage in the right hemisphere can affect memory and have a negative impact on left hemiplegia recovery. For example, memory impairment may cause difficulty following a routine, learning new information, or recalling past events.
Prosopagnosia
A stroke that causes left hemiplegia can also cause prosopagnosia if there is injury to the fusiform gyrus within the brain. Prosopagnosia refers to difficulty recognizing familiar faces and emotions, which can have a negative impact on social life. However, individuals with this condition are often able to identify their loved ones by their voices or other compensatory strategies.
Social communication problems
A lack of empathy or difficulty understanding non-verbal social cues may cause individuals to struggle in social situations following right hemisphere stroke. When accompanied by left hemiplegia, this can cause individuals to have extreme difficulty participating in social or community activities.
Emotional problems
Extreme mood swings and behavioral changes commonly occur after damage to the right hemisphere. Additionally, left hemiplegia often includes paralysis of the muscles of the face, leading to decreased facial expression or a seemingly flat affect.
Spasticity
Also commonly caused by cerebral palsy, spasticity can present on one half of the body and be referred to as spastic hemiplegia. Although muscles are still weak, misfiring of neural signals can cause a muscle to contract, or spasm, which can lead to discomfort and difficulty making rehab gains.
The possible secondary effects of right hemisphere brain injury and stroke vary widely, and no individual’s symptoms or recovery will be identical. However, all survivors affected by left hemiplegia have hope of recovery through a consistent, intentional rehabilitation program. To help you better understand recovery from left hemiplegia, we will review prognosis and treatment methods that can be utilized to maximize rehabilitation.
Is Left Hemiplegia Recovery Possible?
Many individuals with left hemiplegia are able to recover motor control through neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity refers to the central nervous system’s ability to make adaptive changes and rewire its neural circuitry. This allows for functions affected by neurological damage to be rewired to unaffected regions of the nervous system.
Left hemiplegia recovery time depends on many factors such as the location and severity of injury, meaning the recovery timeline will look different for every survivor. Current research shows that the greatest functional recovery takes place in the first six months following stroke onset and in the first three to six months after spinal cord injury. However, there is increasing research supporting the fact that functional improvements can still be made years later in the recovery process.
To recover from left hemiplegia, neural pathways and associated skills can be strengthened through intentional, repetitive practice. Essentially, every skill you consistently practice stimulates the central nervous system and encourages it to make adaptive changes. The more you practice, the stronger the newly rewired pathways become over time.
Therefore, in order to improve movements affected by left hemiplegia, individuals must consistently practice moving the left side of their body. We’ll discuss effective ways to do this in the following section.
Treatment for Paralysis on the Left Side of the Body
For most neurological diagnoses, treatment for left hemiplegia focuses on intensive training of the affected side to promote recovery and neuroplasticity. By working with physical and occupational therapists, individuals can learn effective ways to target their affected muscles and compensate for limited movement.
Passive Range of Motion Exercises
A physical therapist may recommend starting with passive range of motion exercises as this can reduce risk of developing contractures. Passive range of motion involves using your unaffected arm to move your affected limbs or having a therapist/trained caregiver move your body for you.
Although you’re not actively performing the movement, passive range of motion exercises can stimulate the central nervous system. To optimize neuroplasticity, you should actively pay attention to the movements and visualize your limb performing the motion. With enough repetitions, it may be possible to promote adaptive rewiring and gradually regain motor control in the affected side.
Active Range of Motion Exercises
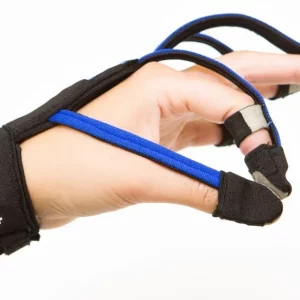
As you advance, your physical or occupational therapist will continue to progress your rehabilitation exercises and will provide you with a home exercise program. This specialized care will help address fine motor skills, muscle strength, range of motion, coordination, and spasticity after left hemiplegia. Additionally, your therapists will help you practice functional movements such as walking and bed mobility, improve efficiency with activities of daily living, and recommend appropriate adaptive equipment.
Electric Stimulation (e-stim)
Therapists may also utilize additional interventions such as electrical stimulation to help survivors recover from left hemiplegia. Electrical stimulation involves placing electrodes over the affected muscles and using electrical input to produce muscle contractions. This electrical input mimics brain signals to stimulate movement and can promote neuroplasticity.
Speech Language Therapy
In addition, speech-language pathologists can provide speech therapy exercises to target the muscles of the face and tongue to help improve speech and facial expression. They can also address dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, which is a common secondary effect that accompanies left hemiplegia.
Ultimately, improving motor control after neurological injury requires highly repetitive and specific practice. Home rehabilitation programs like FitMi can help motivate you to perform the repetitions necessary to improve by turning your everyday exercise routine into an interactive game. Finding fun ways to stay engaged and keep practicing will help you accomplish your rehabilitative goals.
Understanding Left Hemiplegia: Key Points
Left hemiplegia refers to paralysis of the left side of the body caused by neurological injury. While it may be worrisome to experience loss of motor control and sensation, there is potential for individuals to improve their mobility and regain their functional independence.
Through intensive and highly repetitive training, individuals can encourage their brain and/or spinal cord to utilize neuroplasticity and make adaptive changes. Over time, this can result in increased functional independence and improved quality of life for survivors as they achieve their recovery goals. We hope this article helped you understand the causes and symptoms of left hemiplegia as well as the best practices for promoting recovery.